Interpreting the Pandemic for Decision Making and Action
Emergency Planning
MARCH 26, 2020
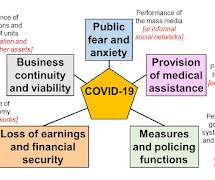
As the Covid-19 pandemic progresses, causing distributed crises in one country after another, it is like watching all I have taught about for the last four decades flash past in a sort of speeded-up film. My primary message was that a pandemic is as much a socio-economic and behavioural problem as a medical and epidemiological one.





Let's personalize your content