A Resilience Charter
Emergency Planning
MARCH 23, 2022
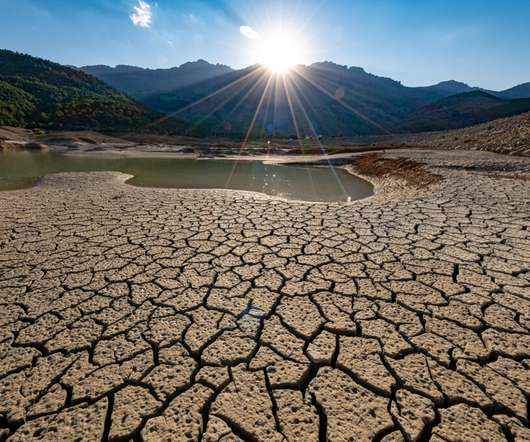
National standards should be developed to ensure that emergency plans are functional and compatible with one another, and that they ensure the interoperability of emergency services and functions. All levels of public administration should be required to produce emergency plans and maintain them by means of periodic updates.







Let's personalize your content