Towards a Taxonomy of Disasters
Emergency Planning
JUNE 9, 2019
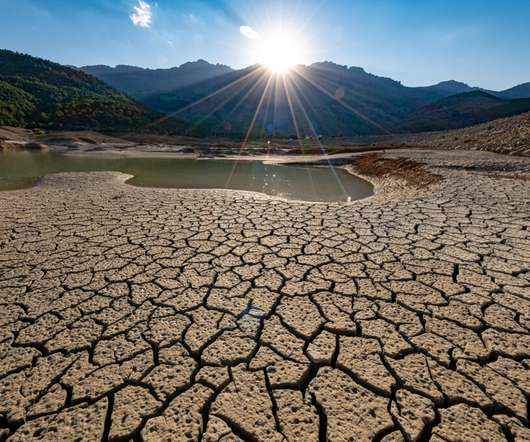
d) Intentional disasters, comprising all forms of terrorism and sabotage. (e) For example, business continuity management has a slightly different set of priorities which induces it to change the emphasis among triggering factors (Elliott et al. Included are toxic spills, transportation crashes and the effects of human error. (c)






Let's personalize your content