Disaster Recovery (DR) Architecture on AWS, Part IV: Multi-site Active/Active
AWS Disaster Recovery
JUNE 23, 2021
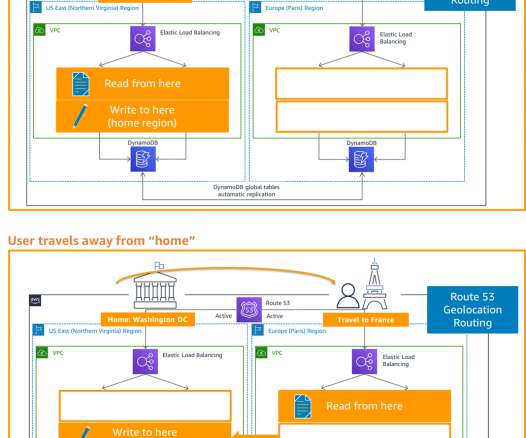
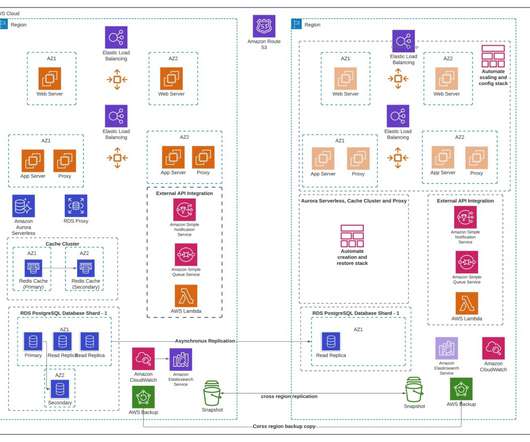
Each Region hosts a highly available, multi- Availability Zone (AZ) workload stack. Figure 2 shows Amazon Route 53 , a highly available and scalable cloud Domain Name System (DNS) , used for routing. If your application cannot handle this and you require strong consistency, use another write pattern to avoid write contention.



Let's personalize your content